Estate tax, also known as death tax, is related to “death”; “The right to pass, transfer or receive property through death” inheritance tax is levied when property is transferred at the time of death. The size of the estate depends on the level of taxation. Inheritance tax includes: An account of everything you owned or had a certain interest in on the day of your death. The fair market value of using these items is not necessarily the cost you paid or the value at the time of purchase “(IRS. gov1)”; total assets; the sum of all these items. Property included in real estate tax may include real estate, annuities, securities, cash, insurance, business interest, trust and other assets.
To calculate the total assets, the deduction and reduction of value may occur, which is the adjusted or “taxable estate” deduction for the total estate Charities with estate management fees, mortgages and other debts, properties transferred to the surviving spouses and qualifications. For qualified real estate, the value of some operational business interests or farms may decrease; (IRS. gov2) After calculating the taxable inheritance amount, add the lifetime value and net amount of taxable gifts to calculate the tax. The comprehensive credit available reduces this tax. For publicly traded securities, cash, assets, jointly owned property and no special deduction, no inheritance tax declaration is required. However, if the total assets are taxed more than “0”, the inheritance tax declaration must be submitted. $1.5 million in 2004-05, $2 million in 2006-08, $3.5 million in 2009, more than $5 million in 2010-11, $5.12 million in 2012, and $5.25 million in 2013; (IRS.gov)
In 700 BC, some people in ancient Egypt also transferred their property according to tax after death. In the past 90 years, great changes have taken place in the real estate tax law. No matter what happens, the federal government always relies on various taxes to provide government funds. The purpose of this research paper is to explain the history of inheritance tax rate and put forward the prediction of future inheritance tax rate.
Inheritance tax has existed for a long time. This was very popular in the Middle Ages, when the king demanded that heirs pay inheritance taxes to obtain the property transferred to them. In Europe in the 17th and 18th centuries, there was a constant debate on whether the transfer of property was a “transfer of property”; Natural rights; when people died, the government did not call the transfer of real estate tax “real estate tax” until the 18th century. It was “unnatural”; it also taxed the transfer of property.
The first real estate tax in the United States was introduced in the Stamp Tax Act of 1797. The Act provides that all documents relating to property such as wills have the right to tax. The introduction of the Stamp Tax Act is an attempt by the government to provide funds for the Great French War. The taxes levied during this period are as follows: The list of the deceased’s remains is charged 10 cents, and the Probate and Administration Department is charged 50 cents. Widows, children and grandchildren can be exempted from inheritance tax on gifts of more than $50; at the end of the war in 1802, the Stamp Duty Act was terminated.
When the civil war broke out in 1862, the return of inheritance transfer tax also followed. During the war, not only the documents, but also the legacies of the dead will be taxed. This bill is different from the transfer stamp duty bill, which includes inheritance tax and stamp duty. During this period, an estate of less than $1000 will be released. In 1864, when military expenditure rose, Congress introduced a gift tax. The gift tax is the property transfer tax that occurs in a person’s life. After the civil war, the tax was also ended.
When the Spanish American War began in 1898, the United States found that it needed more funds, so it reintroduced the inheritance tax. Unlike the other two bills, the 1898 proposal caused a lot of controversy. Taxes are applicable to personal property and inheritance tax is formulated by law. “Small real estate tax-free $10000” In 1901, some gifts were tax-free, including gifts and arts donated to charitable, religious, literary and educational groups, and gifts donated to groups working to prevent child abuse. (IRS. gov3) The war ended in 1902, and taxes were abolished. This tax alone raised more than 14 million dollars.
The inheritance tax and gift tax in 1916 during the First World War were favored by the President. But they also introduced income taxes. At the end of World War I, these taxes were not abolished. In the history of the United States and other countries, there is evidence that there is a direct link between countries in a state of war and tax enforcement. Great changes took place in the tax laws throughout 1916 and 1948. In 1932, the first major change was to increase the futures tax. In the federal tax system of 1932, gift tax became a permanent tax item. Because the parliament realized that the rich could avoid inheritance tax by transferring their wealth while they were alive. The 1932 rule stipulated that donors could transfer US $50000 duty-free during their lifetime, excluding US $5000 per year for each donor. The 1935 tax law provides for the selection of alternative valuation dates. This allows the assets of the deceased’s estate to be assessed within one year of death. With the occurrence of economic events such as the Great Depression, it will be very helpful for citizens to evade inheritance tax. In 1948, another tax bill was enacted. The Act provides for the deduction of matrimonial vicarious and gift taxes. The Act allows surviving spouses who receive legacy property to deduct the value of the property they have acquired. But this inference has limitations. For example, only half of the deceased’s inheritance is allowed.
The next major change in the transfer tax system took place in 1976. The Tax Reform Act is also known as TRA&. “The bill is composed of a single progressive tax rate, which establishes a unified inheritance and gift tax framework for lifetime gifts and wills. Before the enactment of the Act, the cost of leaving property after death was much higher than that of giving property before death. Because the tax rate applicable to futures is very low. The 1976 tax reform act combined the inheritance tax relief and lifetime gift tax relief into a unified inheritance and gift tax deduction, which can be used to offset the donor’s gift tax debt. It is not used at the time of death and can be used to offset the inheritance tax debt of the deceased donor (IRS 122). The person receiving the gift can only receive 3000 dollars per year.
The intergenerational transfer trust (GST) introduced taxes in the 1976 tax reform. In general, the GST ensures that the transfer of the Ministry of Heredity will be taxed on all generations. An intergenerational trust is a legally binding agreement in which donated assets are transferred to grandchildren, not children. Through access to assets across this generation, children are also evading inheritance tax. However, multi generation trusts can still benefit the children of the transferee. Because if any assets of the trust generate income, even if the trust is left to grandchildren, it can also provide income to the grantor’s children.
In 1981, several new amendments were made to the inheritance tax law through the Economic Recovery Tax Act (ERTA) of 1981. The Act allows spouses to be interest free for life, but cannot be terminated. (No. 123 National Taxation Department)
The inheritance tax is a big problem in Washington. Fiscal cliff At the beginning of January 2013, the Senate passed the American Taxpayer Relief Act of 2012. The bill considered inheritance tax. The federal agreement in 2013 stipulated the exemption of gift tax and inheritance transfer tax to be 5 million dollars. The bill also permanently unified inheritance tax and gift tax, so that both have a single progressive tax rate. The bill stipulated that The regulation cannot. The American Taxpayer Act also changed the inheritance tax rate from a maximum of 35% to a maximum of 40%. The current government is promoting the rich to pay their fair share, which often refers to inheritance tax. As of 2013, both the inheritance tax rate and the tax exemption are on the rise. Many Democrats want the exemption to be reduced to $1 million and the tax rate to be reduced to 55%. The tax exemption is so low, the tax rate is so high, and the estate tax will bring huge income to the federal government. After 10 years of tax uncertainty, the new act restored the clarity of the gift and inheritance tax policy, providing certainty for financial planners to implement credible inheritance and gift tax plans in the next few years.
Although the fiscal cliff has passed, the inheritance tax reform is not static. The tax exemption in 2013 was 5.25 million US dollars, calculated by inflation index. These changes have left many problems for people, especially those who are dealing with affairs now. One of the questions they may face is whether spouses should pay inheritance tax when they inherit from each other. The new law allows spouses to deduct an unlimited amount of inherited assets until the death of the second spouse. This deduction applies only to spouses of US nationals. However, the second spouse has the ability to transfer assets tax-free. Widows and widows have the ability to combine all unused assets, while allowing tax free transfers of $10.5 million. This is called portability. The executor of the heritage is responsible for portability. Because this is not an automatic process. Unused assets are transferred to survivors, which in turn become assets or lifetime gifts through the estate. There are several prerequisites for doing so. Even if there is no debt, the inheritance tax declaration should be submitted when the first spouse dies. The due date of this tax return is within 9 months after death. But there is a six-month extension. If the executor fails to submit the tax return or fails to submit it before the deadline, the spouse will lose the right to carry. It is recommended that all spouses file tax returns in this way. Even if they are not rich now, it is only because the future of the tax is unknown. Forbes 1
Lifetime gift tax is expressed in total amount, so it is directly related to inheritance tax. As mentioned above, the current limit of asset transfer in 2013 is 5.25 million US dollars. The combination of the two must be less than the allowance. Otherwise, the successor will bear 40% of the tax. The important thing is that people should know how much of it is used so that the IRS can know when you died. It also provides lovers with the process of breaking up. Tax exemption through sharing in the year of their birth and giving more things to their children during this period; However, if approved, the tax exemption will also be reduced. (Forbes 2)
It is expected that the tax exemption will be greatly reduced soon, and estate planning is essential. For the future inheritance tax rate, this is speculation. Although the laws implemented in 2013 are considered as “laws”, they are “permanent”; This can easily change depending on the country’s leadership in Washington. The current exemptions and tax rates may be permanent, but more restrictions are placed on trusts and other instruments, leaving more people exposed to taxes. Although some states do not have inheritance taxes of any kind, this may change as spending problems become more serious.
Previous projections of the future of inheritance taxes were based on opinion only. But there is a lot of information to support this. President Obama’s recent new federal budget includes an increase in inheritance tax. The President’s proposal will restore the tax rate in 2018 to the level of 2009. These changes will significantly increase the number of families that are required to pay inheritance tax. With the tax rate adjusted to the level of 2009, it is estimated that about 3 out of 1000 people need to pay taxes. It will add about $79 billion in additional revenue in 10 years. As a result of these changes, the per capita tax exemption will be reduced from 5.25 million dollars to 3.5 million dollars this year. This also changed the top tax rate from 40% to 45%.
As a part of the “fiscal cliff” agreement at the end of the year, the Republican Party in Congress insisted on permanently reducing the inheritance tax to a higher level than this, providing the richest Americans with an average tax reduction of $1 million per inheritance. The White House said in the budget: “In addition, wealthy individuals will eliminate some loopholes because they can use complex tax plans to reduce inheritance tax debts. Washington Times 1
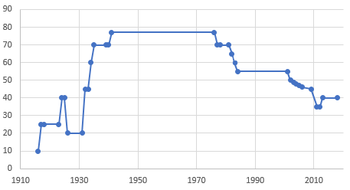
The following figure is basically a simple timetable for the exemption of inheritance tax and tax rate in the United States. The time listed in this table began with the enactment of estate tax in 1916. Since 1916, many significant changes have taken place in the inheritance tax law. The expansion of the 1918 century included how married citizens divided their common property, exercised the right of general appointment, handled 40000 daughters who should be paid to the life insurance inheritance, and deductions from charities. The gift tax was established in 1924. In addition, the main death tax deduction and transfer included in the tax base can be cancelled “the gift tax was abolished in 1926. The gift tax was restored in 1932. In 1935, citizens can now make alternative assessments of property at the time of death. In 1942, the century expanded to include the deceased, paying all insurance premiums, and subtracting the actual expenses of the spouse from the majority of appointments and common property. The common property rule of 1942 replaced the marriage relief of 1948. In 1951, the appointment rules were relaxed. In 1954, the life insurance rules were revised to exclude the insurance that the deceased did not own. In 1976, there was a unified inheritance tax and gift tax. The deduction of orphans, intergenerational transfer tax and transfer base tax have been increased, and special rules have been implemented for small businesses and farms. The deduction for married people will also increase. In 1980, the transfer rule was abolished. In 1981, marital deductions were unlimited. During this period, the tax base has also changed, and the full pension preference and half of the common property are automatically excluded. The system of deduction for orphans was also abolished. In 1986, the company revised the development momentum and increased the deduction amount of the employee stock ownership plan. “In 1987, the hierarchical tax rate and unified credit were gradually abolished for real estate exceeding 10 million dollars.” In 1988, QTIP allowed marriage exemption and revised the inter tax again. It also froze the real estate. In 1990, the property freeze rule was replaced. In 1997, business deductions were made for eligible family businesses, and the right to protect the region was introduced. In 1987, it was abolished and eliminated. In 2001, the Economic Growth and Tax Relief Reconciliation Act was promulgated. As noted above, estate taxes have been volatile.
I personally believe that we will pay more attention to the federal inheritance tax in the future to solve the problem of government expenditure. If Washington maintains its current view of the government, it will need more income and is likely to tax wealthy Americans. If the tax exemption is reduced to the recently proposed $1 million, the number of people who need to pay taxes will increase dramatically.
If Washington does not implement lower tax exemption and higher tax rate, I believe they will try to regulate the way people reduce inheritance tax. In 2013, the maximum annual gift was 14000 dollars, tax-free. This is expected to decline sharply or almost disappear.
source
“Inheritance Tax” IRS. gov.N.p., March 9, 2013, website. April 8, 2013.
Deborah Jacobs; After the Financial Cliff Transaction: Interpretation of the Inheritance and Gift Tax “Forbes.”. Forbes Magazine, January 2, 2013. April 14, 2013.
Boyer, Dave “The Washington Times”: “The Obama budget inheritance tax revives”. N. P., April 10, 2013. Web site. April 14, 2013.